Diabetic sugar is a chronic endocrine disease, characterized by the inability to absorb glucose coming from food and necessary for nutrition, breathing and energy metabolism of cells. In this case, production or interaction with the hormone of the pancreas - insulin is disturbed. It is necessary to regulate the quantitative presence of glucose in the blood. With improper work of a pair of glucose -sensulin, hyperglycemia is a constant increase in glucose. Metabolism suffers, the work of the kidneys, heart, blood vessels and the central nervous system is impaired.
Diabetes
There are two main varieties of diabetes, which, although belonging to a group of endocrine diseases, still have differences.
First type of diabetes (dependent on insulin, youth, inzsd I type)
It is characterized by the fact that for some reason the immune system attacks the beta cells of the pancreas (more than 80%) by producing insulin. There is no hormone, but glucose is supplied to the body with food constantly. Blood sugar comes out of scale. Diabetes of the first type is most often found in childhood or adolescence. But it is not uncommon for adults.
Diabetes of type of type (insulin -dependent, II II II)
Type II diabetes is more often diagnosed in humans after 30-40 years. But the disease is becoming more young. In 90 % of cases, excess weight is observed in patients. The body can still produce insulin, but the sensitivity of cells to insulin is reduced (this is called insulin resistance). A vicious circle arises. Cells do not feel insulin, the body produces even more insulin for eating; cell. Glucose simply accumulates in the blood and insulin increases appetite. One eats, jumps sugar, insulin resistance increases.
Prediabet
Here the glucose level exceeds the reference values, but you cannot even talk about diabetes. Prediabet can become the basis for the development of type II diabetes, as well as diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Gestational diabetes is characteristic during pregnancy. It is most common in II or III trimester.
Also, the course of the disease differs in severity: light (I), average (II) and severe (III).
Diabetes. Symptoms
If you are not in the habit of donating blood for glucose once a year and do not personally know the endocrinologist from the clinic, there are a number of symptoms that can tell you that it is time to contact a specialist. But we will make a reservation immediately, the signs of diabetes are manifested if the insulin deficiency already moves to a critical point. Therefore, at the moment, the most effective way to understand your sugar level is to donate blood.

Diabetes of the first type
Symptoms of diabetes of the first type:
- constant, insatiable thirst;
- dry mouth;
- Frequent urination;
- apathy and fatigue;
- insatiable hunger;
- Weight loss (average 3-5 kg) is not associated with any actions by a person;
- Vision problems (the ambiguity of the picture, as if everything is in the fog).
Diabetes of the second type
The symptoms of diabetes of the second type are similar to type I diabetes in some parameters: it is thirst, hunger, dry mouth, fatigue, vision problems and a frequent desire for the toilet. But this type has its own signs:
- numbness and tingling in the arms and legs;
- Slow healing of wounds and recurrent infections.
The causes of diabetes

Alas, scientists cannot indicate the exact causes of the development of diabetes in humans (especially the first type). Poor ecology, the abundance of viral infections and inadequate function of the immune system are taken as a base. Among the causes of diabetes mellitus are usually distinguished:
- Hereditary predisposition. In addition, the risk reaches 10%if the father has diabetes of the first type and 2, 5%if the mother. If both parents are diagnosed with type II diabetes, then the child is at risk of this disease after 40 years increases to 65-70%;
- an unbalanced diet with an abundance of carbohydrates;
- Excess weight (90% of people with type II Inzsd have it);
- lack of physical activity;
- Stress on a permanent basis;
- prediabet;
- prolonged use of certain drugs (diuretic, hormonal, salicylates, cytostatics, etc. );
- ethnicity (in children of the European race the risk of developing diabetes of 1 type higher);
- History of gestational diabetes;
- Chronic insufficiency of the adrenal cortex.
Complications
This disease is insidious and if you do not follow the doctor's instructions, then complications of diabetes (chronic and acute) may occur, which threaten the work of the whole body. Chronic complications are observed when the high level of sugar lasts for a long time.

The following chronic complications can be distinguished:
- The instability of blood vessels in the retina (retinopathy) leads to a decrease in visual acuity, early development of cataracts or causing blindness.
- In diabetes, periodontitis is common, leading to tooth loss or heart problems. Various infectious diseases of the oral cavity are also possible. You need to monitor hygiene well and regularly visit the dentist.
- Cardiovascular diseases are the most common causes of disability and mortality among diabetics. Angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, stroke and more. The lack of monitoring of cholesterol and glucose levels, increased blood pressure contributes to the development of these complications.
- Nephropathy or destruction of blood vessels in the kidney leads to the failure of functioning or refusal of the kidneys. Ada control is needed.
- Neuropathy (nerve damage). Most often, the risk of neuropathy is exposed to the feet. The walls of the vessels and nerve fibers are destroyed, the blood flow to the legs worsens. The signs of the development of neuropathy are numbness, pain, creeping of geese or loss of sensitivity. Patients, especially the elderly, usually do not attach the importance of what is fraught with the development of ulcers, infectious diseases and amputation. Neuropathy can affect other bodily systems (erectile dysfunction, problems with the gastrointestinal tract, geniopoline system).
- Diabetes is one of the reasons for atherosclerosis as the vessels become fragile, fragile and increase the risk of thrombus.
- There is often joint pain as diabetes leads to a decrease in the amount of synovial fluid.
- It also has a high incidence of mental disorders.
Acute complications that develop rapidly are usually interconnected with fluctuations in blood glucose. Low (hypoglycaemia) and high (hyperglycemia) lead to crises. The crisis of hypoglycaemia (3, 9 mmol/l or lower) manifests itself as a seizure, and hyperglycemic crises are dangerous for the appearance of diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic condition. These are emergency and threatening conditions, leading to convulsions, coma and fatal result.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of diabetes is an important step. In an ideal situation, one must be aware of their glucose level, especially after 45 years. But if it is at risk, then the analysis should be performed more frequently and you need to do it earlier so that you do not miss the valuable time.
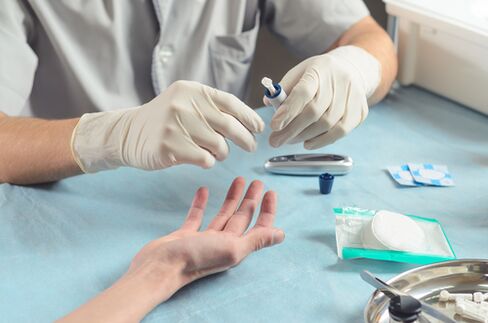
Diabetes is diagnosed in several ways:
- Glycated hemoglobin analysis. The results of the analysis show the average level of glucose in the blood in the last 2-3 months. So you can follow the dynamics;
- Glucose analysis in blood plasma (capillary or venous) on an empty stomach. The audit demonstrates the position of glucose at the moment;
- A glucotolerant test is prescribed in doubtful cases. The test lasts for a long time and involves measuring glucose levels before and after dissolving a glass of glucose water;
- Urine analysis for glucose and/or acetone. A healthy person is not characterized by the presence of these elements in the urine.
Treatment

In the treatment of type I diabetes mellitus, the main treatment of insulin is the main treatment of insulin, which should be administered daily at a dose prescribed and calculated by the attending physician. You can use special insulin syringes, cans syringes or insulin pumps, independently calculating the required dose of the hormone supplied. Under certain conditions, it is possible to prescribe diabetes medicines that stimulate the body to develop its own insulin.
In the first type of diabetes, chip insulin every day, as the passages are filled with the development of diabetic ketoacidosis, which leads to death. Daily insulin + proper nutrition + physical activity can provide life without complications.
In type II diabetes, a doctor prescribes drug treatment designed to reduce sugar levels and normalize a person's condition. Occasionally, insulin replacement therapy may be required, but it is not necessary to take daily. The diabetes diet is observed without failure, as well as an increase in physical activity, control of body weight.
In the presence of prediabetes, the study should be performed once every six months or a year. It is also necessary to get rid of excess weight and switch to diet.
In gestational diabetes, it is necessary to carefully monitor the level of glucose in the blood and to follow the recommendations of the observant physician. Most often, after birth, blood sugar returns to normal. But there is a risk of developing the second type diabetes.
Prediction and prevention
Diabetic sugar is a serious endocrine disease that reduces life by 5-10 years, and men die more often than women. Infectious and viral diseases are more tolerated. Complications against the background of pneumonia, the flu is occurring 6 times more often, compared to statistics from people without diabetes in one history. In healthy people, compared to diabetics, Alzheimer's and other forms of dementia develop more rarely.

But you can and should fight diabetes. Competent management helps them avoid many problems and complications. So, 50-60% of cases of the disease stabilize and do not progress.
Proper control and prevention of diabetes is:
- regular glucose check;
- special diet for diabetes;
- moderate sports;
- Monitoring of blood pressure and cholesterol;
- regular visit to the necessary specialists and undergoing studies;
- Taking medicines prescribed by a doctor.
Diabetes is not fully studied, but medicines and the conscious attitude towards their life with this disease will help to live for a long time and without complications.